-
×
 HP StorageWorks DAT72 USB Ext Drive
1 × AED2,100.00
HP StorageWorks DAT72 USB Ext Drive
1 × AED2,100.00 -
×
 Dell Hard Drive : 146GB 2.5inch SAS (15.000 Rpm) Hard Drive
1 × AED1,639.00
Dell Hard Drive : 146GB 2.5inch SAS (15.000 Rpm) Hard Drive
1 × AED1,639.00 -
×
 Linksys Network Storage System with 2 Bays
1 × AED999.00
Linksys Network Storage System with 2 Bays
1 × AED999.00 -
×
 Dell PowerEdge R410 Intel Xeon E5607 Processor
1 × AED6,609.00
Dell PowerEdge R410 Intel Xeon E5607 Processor
1 × AED6,609.00 -
×
 DIR-685/EEU Wireless 300Mbps N Storage Router
1 × AED819.00
DIR-685/EEU Wireless 300Mbps N Storage Router
1 × AED819.00 -
×
 HP RPS 350/370/380G5/385G2 , 399771-031
1 × AED715.00
HP RPS 350/370/380G5/385G2 , 399771-031
1 × AED715.00 -
×
 ViewSonic TRS10 Conferencing Equipment Kit
1 × AED87,499.00
ViewSonic TRS10 Conferencing Equipment Kit
1 × AED87,499.00 -
×
 External G-SF3 1000 EMEA G-TECH 0G00261
1 × AED1,429.00
External G-SF3 1000 EMEA G-TECH 0G00261
1 × AED1,429.00 -
×
 LOGIYECH HEADSET USB H340
1 × AED109.00
LOGIYECH HEADSET USB H340
1 × AED109.00 -
×
 WD ROUTER WIFI MY NET N900 CENTRAL WITH 2TB HDD BUILT IN STORAGE480.00
1 × AED609.00
WD ROUTER WIFI MY NET N900 CENTRAL WITH 2TB HDD BUILT IN STORAGE480.00
1 × AED609.00 -
×
 HP StorageWorks 8/8 Base SAN Switch
1 × AED16,679.00
HP StorageWorks 8/8 Base SAN Switch
1 × AED16,679.00 -
×
 HPE Aruba 2930M 48G PoE+ 1-slot Switch – JL322A
1 × AED13,199.00
HPE Aruba 2930M 48G PoE+ 1-slot Switch – JL322A
1 × AED13,199.00 -
×
 5-Port Network Switch (10/100 Mbps)
1 × AED119.00
5-Port Network Switch (10/100 Mbps)
1 × AED119.00 -
×
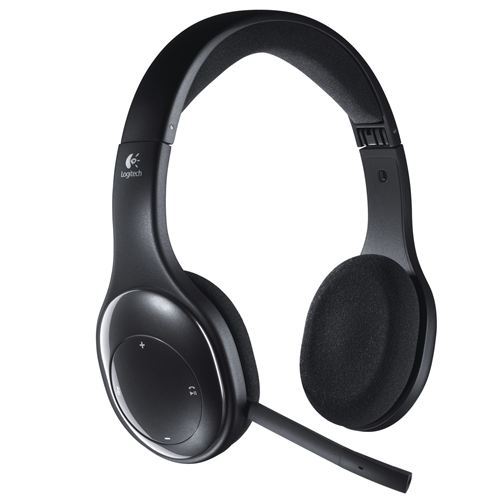 LOGITECH HEADSET BLUETOOTH H800
1 × AED359.00
LOGITECH HEADSET BLUETOOTH H800
1 × AED359.00 -
×
 Dsan Video Clock VC-2000LT Cat5 to USB Adapter for Limitimer
1 × AED1,499.00
Dsan Video Clock VC-2000LT Cat5 to USB Adapter for Limitimer
1 × AED1,499.00 -
×
 TD-8816 1 ethernet port ADSL2+ router with bridge and NAT router
1 × AED79.00
TD-8816 1 ethernet port ADSL2+ router with bridge and NAT router
1 × AED79.00 -
×
 Dell 600GB SAS 6Gbps 10k 6cm (2.5") HD Fully Assembled
2 × AED2,219.00
Dell 600GB SAS 6Gbps 10k 6cm (2.5") HD Fully Assembled
2 × AED2,219.00 -
×
 WD ROUTER WIFI MY NET N900 CENTRAL WITH 1TB HDD BUILT IN STORAGE345.00
1 × AED439.00
WD ROUTER WIFI MY NET N900 CENTRAL WITH 1TB HDD BUILT IN STORAGE345.00
1 × AED439.00 -
×
 Connectix 100mm 1u 10" Shelf
1 × AED99.00
Connectix 100mm 1u 10" Shelf
1 × AED99.00 -
×
 HP StrorageWorks DAT72 USB Int Drive
1 × AED1,999.00
HP StrorageWorks DAT72 USB Int Drive
1 × AED1,999.00 -
×
 Samsung ML4550B Toner for ML4550 ML4551 N ML4551 ND ML4050 N
1 × AED699.00
Samsung ML4550B Toner for ML4550 ML4551 N ML4551 ND ML4050 N
1 × AED699.00 -
×
 AP1050DN-S - Huawei Indoor Access Point
1 × AED3,199.00
AP1050DN-S - Huawei Indoor Access Point
1 × AED3,199.00 -
×
 WD Black 500GB Performance Mobile Hard Disk Drive - 7200 RPM SATA 6 Gb/s 32MB Cache 7 MM 2.5 Inch WD5000LPLX
1 × AED299.00
WD Black 500GB Performance Mobile Hard Disk Drive - 7200 RPM SATA 6 Gb/s 32MB Cache 7 MM 2.5 Inch WD5000LPLX
1 × AED299.00 -
×
 PRIVACY PANEL FOR SYMMETRA PX AND XR FRAME – ACDC1008
1 × AED2,599.00
PRIVACY PANEL FOR SYMMETRA PX AND XR FRAME – ACDC1008
1 × AED2,599.00
Subtotal: AED148,232.00
 04 3550600
04 3550600 052 7036860
052 7036860






There are no reviews yet.